Whether you just forgot or procrastinated, don’t worry. We found some great last-minute deals on gifts Dad will love.
Category: Tech news
hacking,system security,protection against hackers,tech-news,gadgets,gaming
New York City Flexes Again, Extending Cap on Uber and Lyft
Officials want to extend the city’s limit on the number of for-hire vehicles, and may consider a congestion charge.
‘Sign In With Apple’ Earns Mixed Reactions From App Makers
Soon, you’ll be able to log into third-party apps using your Apple ID. The move has its fans, but also its critics.
Where is the EU going on tech and competition policy?
Huge technology policy questions are looming for whoever takes the top jobs at the European Union in the coming months. Decisions that could radically reshape tech business models, reconfigure the competitive landscape and change the relationship between Internet users and the content and services they consume.
In short, the entire future of the tech industry — and potentially not just in Europe but worldwide — is at stake.
The incoming European Commission will be faced with a lengthy list of pressing questions. How will they reboot competition law for the digital era? Should they rush in swinging a break-up hammer at monopolistic tech giants or take a scalpel to the competition-crushing problem of networked dominance by slicing up their data flows?
They will have to defend fundamental rights that call for privacy by design and data minimization against AI’s rapacious demand for data and the predictive powers of pattern-spotting algorithms.
They will have to evaluate how to make sure platforms play fair — and ensure that the initial embrace of sellers or service providers doesn’t evolve into crushing abuse. They will have to fashion rules that can wrap around digital giants, rather than getting bent out of shape by ‘winner takes all’ business models.
The power of tech giants to influence entire nations is now writ large in EU domestic politics. Europe knows it needs to hammer out an agreement on reforming digital taxation, with rising citizen anger over tax inequalities. The question is how to do it when certain states with low corporate tax rates have been colonised by tech giants which definitely don’t want tax reform to happen.
There’s also the tricky business of arbitrating between Europe’s traditional creative industries and the predominantly US sharing platforms that have gotten fat off of the back of others’ content — a battle so fraught it’s already yielded an EU copyright reform as polarising as Brexit.
How, too, to level the playing field between Internet giants and traditional telcos?
That requires winning agreement on an update to ePrivacy rules that’s been stalled for months. Because, again, new rules are urgently needed — to wrap around digital comms and address digital marketing’s weed-like sprawl, an outgrowth that’s spawned an entire shadowy industry of trackers, data brokers and people profilers which can be linked to many a data scandal and has driven EU consumers into the arms of ad blockers. How to find a way through all the competing interests to bring order to the unregulated mess that is modern adtech?
Then there’s hate speech and online disinformation. What’s to be done to shrink the democratic risks of political manipulation without trampling freedom of expression? And how can Europe best equip its citizens for the next waves of deepfaked information warfare while also getting platforms to accountably clean up their act?
Europe needs to shape a strategy to support AI too. It wants to do this in a way that reflects and bakes in European values. But how to ensure ethical guardrails to make AI development sensitive and “human-centric” don’t just end up kneecapping homegrown technologists versus whatever’s coming out of China?
Speaking of China, then of course there’s 5G. The Commission has to chart a delicate course between member states’ national security priorities and the fragmentation threat to its flagship digital single market policy if EU nations respond differently to Huawei. The whole project risks collapsing into mutual mistrust — which would reverse the intended gains to Europe’s digital economy.
On the legal front, an ongoing clash of priorities between US surveillance practices and EU fundamental rights also looks like trouble brewing.
A flagship EU-US data transfer mechanism launched by the Commission in 2016 is now facing serious legal questions. Does the next Commission have with a plan B to keep critical business data flowing for the thousands of companies signed up to its Privacy Shield framework if it gets struck down by a judge’s pen?
This is not a theoretical threat; the predecessor arrangement that had stood for fifteen years was invalidated in 2015, after a legal challenge which drew on NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden’s revelations of US mass surveillance programs. Trump’s ‘America First’ policy agenda clearly risks exacerbating this clash.
The US president is also of course continuing to rain down trade uncertainties that are rocking the stability of East-West technology supply chains. How should Europe respond to the wreaking ball potential of Trump’s trade war? What support can it offer its own tech industry to manage a level of uncertainty that makes brexit look like a picnic?
And, as the Internet splinters into increasingly localized flavors, how will Europe prepare and position itself?
The techie to-do list crossing the next Commission’s desk is packed with highly charged, pressing and politically fraught problems.
Over the past year the EU has dined out on making a name for itself on the world stage with a shiny new set of digital privacy rules — aka, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) — at a time when US policymakers are just waking up to the rude incursions of homegrown data-mining tech giants. But attention now needs to be paid to ensuring it actually delivers what was promised or else the global spotlight will be pointing at policy failure.
So yet another task for the next Commission will be applying the right level of strategic pressure to make sure the regulation’s wheels are turning.
National data protection agencies are where GDPR enforcement will fly or fail. The highest profile cases that will really test their mettle are of course attached to tech giants — including Facebook and Google. The latter’s handling of personal data for behavioral advertising is now under scrutiny in Ireland.
The Irish DPC also has more than ten open investigations into Facebook-owned businesses, covering a range of issues — from probes of specific security breaches to whether it is lawfully gaining consent to process the data of users of its platform being as it offers no opt-out from behavioural ads.
If Ireland fails to defend European values and rights against the commercial incursions of some of the world’s most powerful companies it would represent EU policy failure at the highest level.
It could also invite revolt from less conflicted parts of Europe. A dispute resolution mechanism is baked into GDPR, which allows the European Data Protection Board to step in if disagreement between DPAs om cross-border cases threatens to derail decisions. While this does look intended as a tool of last resort, the market denting power of tech giants is piling the pressure on — with record numbers of such complaints awaiting judgement.
Either way, battles are brewing. And the biggest fight looks to be for the future shape of the commercial Internet.
Ad-funded business models that have been allowed to grow like weeds are under regulatory scrutiny like never before — thanks, in large part, to European interventions. So too are the tech giants that have profited so handsomely by being able to use data how they like.
At the same time a new generation of privacy-conscious startups is thinking differently and doing what it can to gain footholds in markets where platform giants suck most of the oxygen out of the room.
Strong decisions by the next Commission to defend European rights and reboot digital markets with fairness and competition at the center have the potential to transform the digital economy so that there are far more winners, not just a few taking all.
The question is whether Europe’s leaders will rise to the challenge.
Who’s in the running to be the next EC president?
The center right’s preferred candidate — and therefore the technical favorite for the EU’s top job — is German conservative, Manfred Weber.
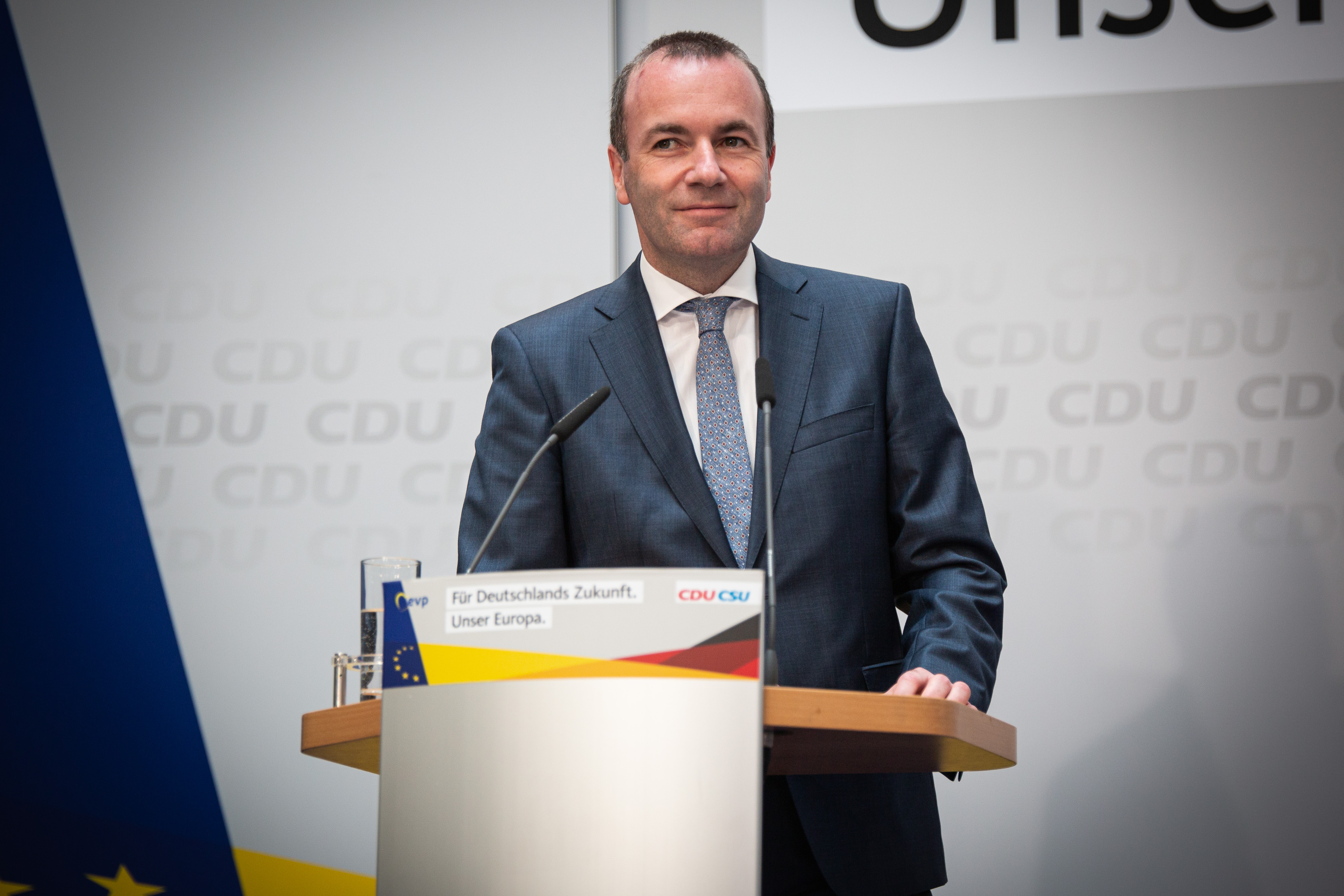

Manfred Weber. Photo by David Speier/NurPhoto via Getty Images
In Commission president candidate debates he has billed himself as offering “stability” for the European project, via a “pro-compromise approach” — and talked about strengthening “the innovation field” as the key to building a stronger EU economy, saying he also wants to upgrade the EU-US trade relationship to bolster Europe’s prospects.
But Weber has a lack of executive experience and suffers from something of a charisma vacuum at a time when a big personality might well be required to sit in the chair and ‘sell’ the next Commission to a more fragmented European Parliament.
The kaleidoscope twist of European parliamentary politics may also have undermined Weber’s frontrunner chances by allowing critics to argue against him on the grounds that his party, the EPP, failed to grow its share of the votes. So it may be that another European People’s Party candidate comes through in the end. One who offers a finer-grained political compromise.
The EU’s chief Brexit negotiator, Michel Barnier, looks to have potential — and is being tipped by some of the current political chatter — having played a high profile role in recent European politics, calmly handling the chaotic mess produced by the UK’s 2016 referendum vote to leave the EU.
More importantly, perhaps, Barnier is French. One of the EU’s powerful national leaders — France’s president, Emmanuel Macron — has been seeking to assert authority over the parliament by indicating he won’t be bound by a system of preferred candidates put forward by its political blocs.
That’s bad news for Weber, but it could lift Barnier out of the wider field if Macron prevails in stamping France’s mark on the Commission presidency.

Michel Barnier. Photo by Thierry Monasse/Getty Images
Although plenty of other establishment names are still being bandied around for the top job — including chair and MD of the International Monetary Fund, Christine Lagarde (also French); and Dutch PM, Mark Rutte, to name just two.
It’s certainly hard to imagine a more symbolically safe pair of hands for the EU to choose for its top job right now than Barnier: The man tasked with holding the EU together in the face of the threat posed by Brexit.
Brexit risks not just the UK’s stability but could very well scatter wider seeds of destruction if it erodes and destroys the cohesion required to keep the European project together. So Barnier’s proven ability to glue the 27 remaining Member States on a common negotiating path could be seen by EU leaders as having strategic appeal.
What his presidency might mean for wider EU policy is less clear, though, given his focus on Brexit has kept him out of the fray — and away from participating in public debates with some of the proposed candidates.
The center left’s pick for president, Dutch politician Frans Timmermans, would need to prevail against the dominant EPP bloc to succeed in getting the nomination. Which likely means persuading a strengthened liberal contingent to throw its backing behind a ‘progressive alliance’ of socialists and liberals.
While possible, it looks to be a challenge.
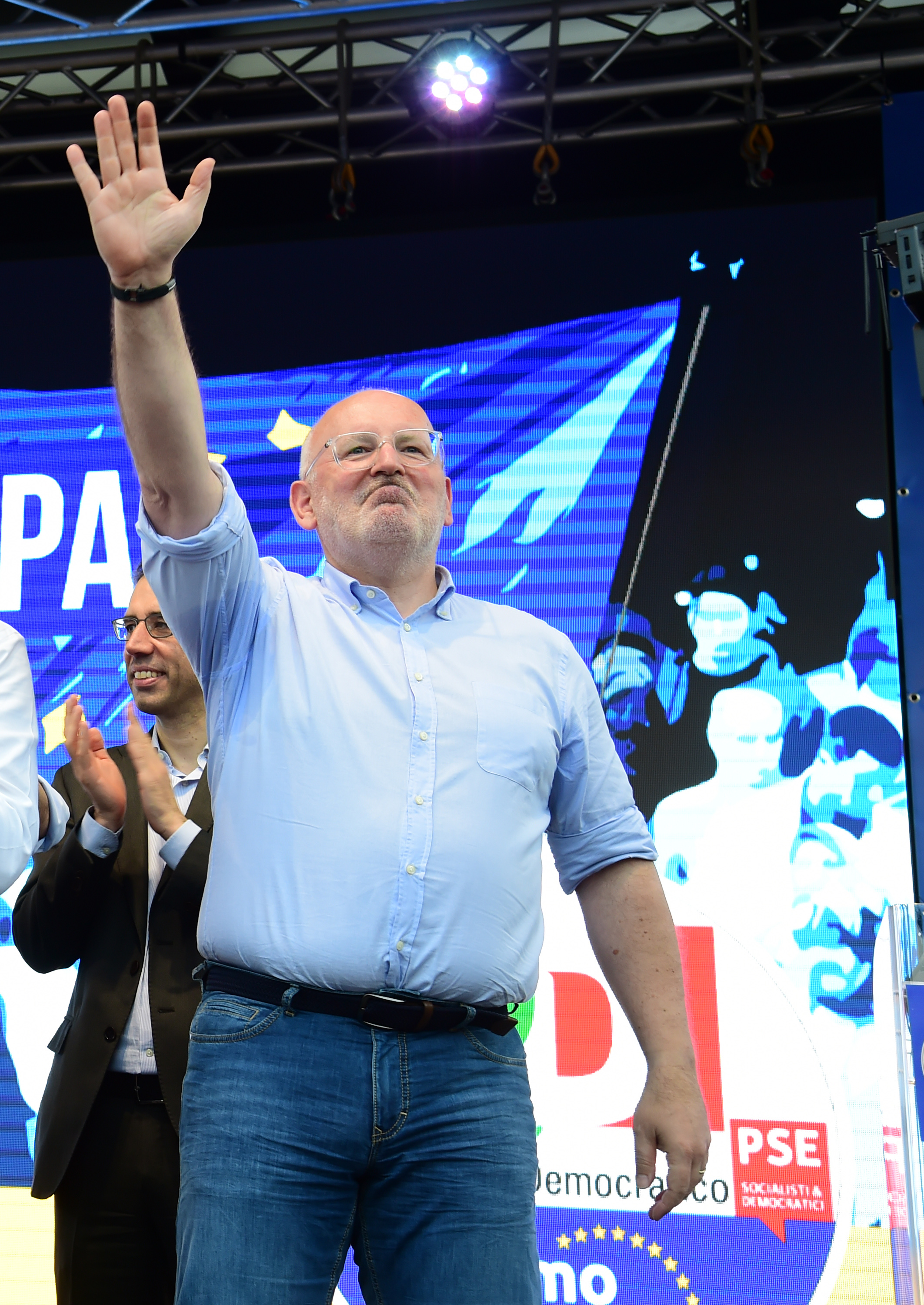

Frans Timmermans. Photo by Pier Marco Tacca/Getty Images
Timmermans has made a public pitch as a change candidate, saying Europe needs more social justice and sustainable social policies — including putting taxing tech giants front and center of his talking points, and dubbing it “unacceptable” that some companies have gotten so big they can “arm twist” entire Member States to vanquish taxes.
Climate policy is another stated focus. He has called for stepped up efforts to enable a European-wide viable carbon tax plus quicker transformation of the energy sector as well as suggesting new ideas in agriculture — such as switching to more sustainable food production.
He has also said he wants to see a corporate tax rate floor across the EU, and called for every state to implement a minimum wage. An articulate and at times impassioned speaker, Timmermans posses at least some of the charisma Weber lacks — even while he faces plenty of political hurdles.
An outside bet — who has betted against big tech…
For those who like an outside bet, the more fragmented European Parliament vote may have buoyed the chances of liberal candidate for Commission president, Margrethe Vestager — who could emerge as a compromise alternative since the liberals grew their presence in parliament (and her own party in Denmark did well in national elections).

Margrethe Vestager. Photo by Thierry Monasse/Getty Images
Although she is just one of a full slate of candidates fielded by the liberals, which also includes another prominent EU politician, MEP Guy Verhofstadt — who has also made his ire over big tech’s rights incursions felt when he heckled the Facebook founder last year, when Zuckerberg addressed some MEPs and failed to answer most of their questions.
Few can compete with Vestager’s profile on that front though.
The EC’s current competition commissioner has gained fame on both sides of the Atlantic for going after big tech, including issuing three high profile antitrust decisions against Google, such as a $5 billion fine for Android as well as action on EU illegal state aid that saw the Commission order Apple to pay $15 billion in back taxes to the Irish state, covering a decade of unpaid taxes. On her order, Amazon also got hit with a large illegal tax benefits bill, and may yet face antitrust action.
As a result of holding a key office and how forcefully she has spent her time as antitrust chief, she remains one of the most high-profile European commissioners.
Asked about what she would offer as Commission president she has said “you have to be forceful to serve people well.” Naturally, she is pro-regulation — a sentiment that chimes well with rising public concern over unfettered and even feckless Internet giants. But while demonstrably forceful, she is also thoughtful and methodical, and can’t be accused of jumping on the bandwagon of populist positions.
She’s also shown her steel in office, issuing competition decisions that have angered powerful heads of EU states — which might therefore have been politically disadvantageous to her prospects of further advancement in the Commission.
Towards the end of her time as commissioner, she instigated a review of competition policy to respond to the challenges posed by digital markets, signaling a reform agenda. She has also talked publicly about regulating data flows as a more intelligent route to regulate big tech versus swinging the hammer to break companies up.
A Commission headed by Vestager would surely have a strong appetite for stamping its mark on digital regulation. At very least it would drive discussion, even if winning consensus on pan-EU digital reforms may be more difficult to achieve (especially on a highly divisive issue like tax reform).
In public debates of Commission presidency candidates, Vestager has said that increasing diversity and managing climate change would be priorities if she took the top job, emphasizing too the need for an inclusive transition to a sustainable economy.
Given her high personal profile, it seems at least reasonable that should she miss out on the top job she will end up with another major post, such as vice president. It would also, of course, signal progressive change if European institutions were to appoint a woman to one of the top jobs for the very first time.
It’s also not inconceivable that she could be reappointed as competition commissioner, given how she has owned the office.
Either way, Vestager’s influence on competition policy looks very unlikely to fade — not least because similar ideas are catching fire across the Atlantic.
At this stage, though, all is still in play where the Commission presidency is concerned.
More clarity may emerge after the next meeting of EU leaders, on June 20 and 21, when the Council will convene to discuss nominations — and adopt a first draft of their strategic agenda for the next five years.
What’s on the EU Council’s strategic agenda?
An outline of discussion topics for this agenda last month included, among myriad talking points, Europe’s migration challenge; tackling online disinformation, bolstering cybersecurity and addressing hybrid security threats; deepening and strengthening the single market and developing an industrial strategy, as well as investing in skills and education, promoting innovation and research.
Ensuring fair competition was also on the list.
A section on “building a greener, fairer and more inclusive future” suggested accelerating the energy transition and investing in “mobility of the future” among its listed points.
While a section entitled “embracing the digital transition” cited developing AI, promoting “access, sharing and use of data,” and ensuring connectivity as key talking points.
Elsewhere the document talked about defending European people’s rights and freedoms, and indeed projecting European values on the rest of the world. But with so many power games still to play out, the shape of Europe’s future tech and competition policy remains just that: A draft, with priorities hard to predict.
“It’s most unlikely that there’s going to be any reversal of major policies,” suggests Dr. Alistair Jones, an expert on EU political policy at De Montfort University. “What we are likely to see — and this is pure conjecture — is assuming Brexit goes ahead (and that’s still an if) then what we’ll probably see is a Commission being a little bit more tentative on the integration process and wanting to go forward more gradually on integration to keep everyone on board.
“So things like the digital market will proceed, slowly and carefully. I don’t see a huge lunge forward in greater integration on any aspects. I think it’s going to be very tentative, very much small steps.”
Online disinformation is an issue where the EU does have serious concerns. The Commission has been paying close attention to how platforms are responding to increased pressure, via a (for now) voluntary code of practice — setting up a monthly monitoring requirement for them to deliver progress reports, and issuing sharp rebukes that progress hasn’t been good enough.
But a pan-Europe regulatory response to online muck spreading is complicated by whether it’s an EU or national competence.
“The problem is it probably lies with the national governments and they are loath to want to give greater responsibility to the EU in this area because they have their own ways of doing things,” says Jones.
The Germans, for example, haven’t been shy about passing a law to punitively punish platforms if they fail to swiftly remove hate speech, while the UK remains focused on devising a framework to control a broader range of online harms.
Where online content rules are concerned, Europe’s cultural differences suggest that this sort of policy patchwork will remain the norm.

Image via Getty Images / AdrianHancu
Similarly, Jones believes core decisions on regulating 5G will remain at a Member State level — with the Commission likely only moving to set a future floor for trans-national EU minimum standards, rather than seeking to impose hefty security restrictions on procurement decisions.
“As it moves forward, I can see the Commission — as it’s done in the past — taking over a broad brush big picture regulatory role,” he says. “So who can be involved in the delivery of 5G, which businesses are involved, things like that. I can see as it is rolled out the Commission and the EU collectively wanting a degree of consistency, and that links to single market rules, it links to competition rules, it links to commercial policy rules. Some of that’s already in place but at the same time there may be a need for greater policing that further down the line.”
One issue that does generally cut across the political spectrum is digital taxation, though achieving agreement on that front may be hampered by a political requirement for the EU to be more sensitive to concerns about increased integration — and not be seen blindly pushing on the accelerator.
Again, says Jones, Brexit complicates matters. He suggests a more broad-brush approach may win out in the near term, such as the Commission looking at the operation of the entire single market — “and how that can be done more effectively and efficiently” — rather than trying to tackle head-on national resistance if the EU pushes to get input on Member States’ tax systems.
“It’s something that may bubble along just below the surface,” he posits of digital tax reform. “Maybe in five years times, after the next elections, [there could be a] big package to possibly change the whole taxation system of the EU. And it may be that it gives the EU some input into national taxation policies but that is going to be resisted by some countries.”
Some Member States have voiced loud concern about digital tax inequality. Including France and the UK, which are pursuing their own flavors of reform. Though without a pan-EU approach there’s no real chance of addressing the problem.
Getting political agreement on that will be difficult, with smaller states having lucratively leveraged a low tax economy to pull in the tech giants. So the Commission may remain caught in the middle.
“We often assume that the Commission sets the policies. The Commission don’t. The Commission tries to mold the agenda but it’s up to the Council’s ministers and also the European Parliament to take that forward,” says Jones. “So if we have a Commission that’s willing to say — ‘hey, digital economy, the EU needs to have greater involvement in all of this’. The national governments have got to buy in. And if they don’t buy in it doesn’t matter how good the commissioner is, it doesn’t matter how farseeing they are, they’re not going to get anywhere. So there’s got to be this ability to get buy-in from the Member States.”
That said, individual commissioners can be key to driving a particular reform agenda. So the personalities and expertise involved can make a big difference — if it helps them win the support of member states.
“There probably is going to be more appetite for big tech regulation but the problem they’ve got at the Commission is that at times, collectively, their head is stuck in the sand and they are loath to go forward on a number of issues,” says Jones. “It may be up to individual commissioners who have got that individual get up and go, that individual vigor, that knowledge of the area they are in charge of — it may be the individual commissioners who may actually drive things forward.”
“It may be there’s a commissioner in the digital economy who’s going to grow into the role, if they’re not already there,” he adds. “But what they will need is the support of the individual member states.”

Image via Getty Images / KatarzynaBialasiewicz
After the Commission president, the competition commissioner role stands out as a critical appointment, given its high degree of autonomy and power. Whoever lands the brief will certainly be one to watch, not least for how they respond to growing political appetite over the Atlantic to crack the back of tech giants’ platform power.
A future date to look out for on that front is when the nominee for the EU antitrust brief gets questioned by the European Parliament — both to see how they respond but also what kind of questions they face. That will offer a flavor of the new parliament’s priorities for regulating competition.
A parliament signalling it wants more action to rein in big tech could act as fuel for the next commissioner, says Jones.
The EU’s next antitrust chief will also have on their desk the review Vestager instigated of digital markets — so it will be up to them to make a call on how to take that work forward. A decisive commissioner could have a major impact on digital markets and business models. So it’s a critical appointment.
But again we’re still a long way off knowing who the person will be. Not least because individual commissioner appointments can depend upon how big a personality the Commission president is.
“If you’ve got a big personality who can drive things through with the support of the European Parliament they can get the national nominees into the places that they want,” says Jones.
“This is the problem that the president has — they do not know who the individual nominees are going to be from which Member States. So until they know who the nominees are from which Member State and then what portfolios they may be appropriate for — what portfolios they want to give them — it’s all up in the air.”
How is the next Commission president decided?
Multiple candidates remain in the running to take over from Jean-Claude Juncker as Commission president come November 1. Though even that timeline is not 100% certain. If, for example, MEPs take a dislike to a Council pick for president they can reject the whole Commission, delaying the entire process.
The process for deciding the next Commission president involves a nomination, by a qualified majority, from the European Council that’s required to factor in the result of the most recent European elections.
Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) then vote on the choice — with an absolute majority required for the Council’s nomination to prevail.
While the Commission’s top job is influential, as regards shaping pan-EU policy — with the president responsible for setting political direction and chairing their cabinet of commissioners atop the various policy areas — the office shouldn’t be thought of as the equivalent of the president of the United States. But is a key strategic role. Collectively, the Commission executes on a pan-EU legislative program. It’s responsible for drafting the budget and is the only EU institution that can propose legislation.
The European Council is the power behind this throne, feeding in whatever policy priorities can be agreed by a roomful of heads of government/state of the EU’s (currently) 28 members — in addition to playing kingmaker by nominating their choice for Commission president.

Image via Getty Images / Dado Daniela
There is also a president of the European Council, who works to seek consensus between Member States. This position is set to change shortly too, via election by Council members, albeit for an initial term that’s half as long as the Commission president.
Nominations for the various European commissioners typically involve large amounts of horse-trading and power playing for portfolios between the Member States.
The aim is for the Commission to contain representation across the bloc, factoring in regional differences in politics, nationality, north vs south, east vs west, diversity and so on. But it’s a political compromise, never a flawless mirror.
In practice, the selections of Commission nominees can be a surprising process in which little known figures can suddenly find themselves with the right combination of strategy, nationality and diplomacy to unlock the right support.
With so many balancing and compromise factors in play, the make-up of the next Commission is always complex and hard to predict, and arguably more so this time around, given wider shifts in the European political landscape — including ongoing ructions caused by the UK’s vote for Brexit — adding extra layers to the usual palimpsest.
A more fragmented European politics
Elections for the parliament were held last month and the vote returned a more fragmented hemicycle — weakening the traditional center-right and center-left blocs that have dominated for 40 years. Although they still remain the major political forces it’s the liberals, greens and nationalists that gained ground.
A more fragmented parliament suggests reaching consensus on both the shape of the next Commission and what legislation it will go on to propose could prove more difficult unless new political alliances can be forged. At this stage, it’s not clear what the new European parliament voting blocs will be.
There remains a risk that EU legislative processes could be stalled if compromise can’t be reached across a differently stripped spectrum of divergent political positions.
“We don’t really know what the groups are going to be in the European Parliament,” says Jones. “Those groupings are fluid. So if you look for example at the Brexit Party going in with the Europe of Freedom and Direct Democracy — when Britain leaves, that whole grouping disintegrates. Because they’d only have six countries represented. They’d need seven.
“If that’s the case it may be that some of those party groups may look elsewhere… We simply don’t know. So how the actual structures of the smaller parties are going to be — that is up in the air. Until that is resolved, the whole establishment of the Commission beyond the presidency is up in the air as well.”
“Everything’s up in the air at the minute,” he adds, noting just one certainty: That the two major parties still dominate, despite their vote shrinking.
“If they have organized things so that there’s an agreement that whichever party has the most seats their nominee for the presidency for the Commission would go forward,” Jones suggests. “If they stick with that, then the starting point of establishing the Commission presidency means that the EPP will keep their person in place.”
The full phalanx of Commission president and commissioner appointments has also got to be approved by the European Parliament, en masse — with MEPs getting a vote to either accept or reject.
“So what you’ve got therefore is a huge haggling process. And this is why when people say there’s a fragmented European parliament we don’t know what’s going to happen — they’re absolutely right. Until the groups are actually sorted in the European Parliament then we’ll get a better idea of the power structures, and then we’ll get a better idea in relation to with the presidency having been sorted how the rest of it will flow through.
“It could be — could be — really problematic in trying to get a Commission membership through if the smaller groups in the European Parliament work together to try to block appointees they could cause problems.”
So, again, much hangs on who will be the next Commission president, and how persuasive they prove across a more fragmented political landscape. As noted earlier, Barnier’s negotiating glue may look like a handy special power. Although, as a personality, he’s hardly overflowing in the force of character department — famed only for having an unnerving stare.

Image via Getty Images / robertiez
Jones takes the view that the policy agency of the next Commission isn’t likely to emerge until Brexit itself has happened — assuming, of course, that Brexit does actually go ahead. (And where Brexit is concerned there are still absolutely no guarantees at all.)
“When/if Britain leaves the entire power structure in the European Parliament could change. Because the Freedom and Direct Democracy Group could collapse with Brexit leaving that group [assuming the party follows the UKIP template and involves itself with the same group]. So everything is up in the air at the minute. That will get resolved, probably by if we’re lucky the middle of next month.
“Then you start on the commission appointments and it’s the summer — and some of the countries effectively shut down. So it may be that it’s September or possibly even early October that we’re going to see this entire process completed. That’s the nightmare scenario. So the EU basically flounders for the next three to four months.”
Meanwhile, if muscle-flexing Macron misses out on a French Commission presidency it’s conceivable he could push for the powerful antitrust portfolio as a consolation prize. Which perhaps lends some color to Facebook’s recent attempts to cozy up to the French government to work on ideas for Internet ‘co-regulation.’
Zuckerberg may be placing his own bets on the future shape of the Commission by seeking to make powerful French friends in the hopes of influencing pan-EU policy before the next commission has had chance to take shape.
But where EU politics is concerned, the phrase that’s been repeated ad nauseam of the Brexit negotiations applies here too in spades: ‘nothing is agreed until everything is agreed’.
This time around Europe’s political dial the risk of disagreement appears to be zooming alarmingly into view. So the real test of the European project will be whether it can weather disruption to its usual philosophy of onwards and upwards — its political push for ‘more Europe’ — when some of its people are voting for less.
If the EU can’t carry all its people along there will be little hope of driving any major policy agenda — which means key questions of technology and competition going unaddressed, generating legal uncertainty and compliance risk for business with knock-on economic effects.
Tech giants have the resources to manage political uncertainty — indeed, they’ve shown themselves adept at exploiting political vacuums and blindspots — so it will be startups and the next generation of entrepreneurs that get failed.
Consensus works until it doesn’t, as the UK’s Brexit schism illustrates. So there’s a clear cautionary tale for the EU powers that be — if they can but put their heads together and listen.
“The issue is going to be how the rest of the European countries work together. Because although [the UK is] a reluctant European, and we’re never very keen, one of the roles that we played was as a break on some of the more excessive integrationist ideas that might have arisen from the Commission that some of the other big countries such as France and Germany bought into,” says Jones when asked whether he thinks the European project can survive Brexit. “With that role going, assuming we leave, it does give the EU the opportunity for the EU to drive forward for greater integration — and it may be that we see the development of a two-speed Europe. If that happens the whole project will disintegrate. Of that I am convinced.”
“They need to be taking on the more reluctant members,” he adds. “So the Hungarys, the Polands, the Czech Republics… as well as the more integrationist countries, such as Belgium, such as Luxembourg, such as Germany and France. They’ve got to be taking everybody along together… Everybody’s been dragged along a bit reluctantly. They’re going to have to be a little bit more considerate if Brexit goes ahead because otherwise the project could disintegrate.”
Gadget Lab Podcast: The Biggest News From E3
Peter Rubin joins the show this week to tell us about the major announcements made at the videogame industry’s big conference.
Amazon Spark, the retailer’s two-year-old Instagram competitor, has shut down
Amazon’s two-year-old Instagram competitor, Amazon Spark, is no more.
Hoping to capitalize on the social shopping trend and tap into the power of online influencers, Amazon in 2017 launched its own take on Instagram with a shoppable feed of stories and photos aimed at Prime members. The experiment known as Amazon Spark has now come to an end. However, the learnings from Spark and Amazon’s discovery tool Interesting Finds are being blended into a new social-inspired product, #FoundItOnAmazon.
Amazon Spark had been a fairly bland service, if truth be told. Unlike on Instagram, where people follow their friend, interests, brands like they like, and people they find engaging or inspiring, Spark was focused on the shopping and the sale. While it tried to mock the Instagram aesthetic at times with fashion inspiration images or highly posed travel photos, it lacked Instagram’s broader appeal. Your friends weren’t there and there weren’t any Instagram Stories, for example. Everything felt too transactional.
Amazon declined to comment on the apparent shutdown of Spark, but the service is gone from the website and app.
The URL amazon.com/spark, meanwhile, redirects to the new #FoundItOnAmazon site — a site which also greatly resembles another Amazon product discovery tool, Interesting Finds.
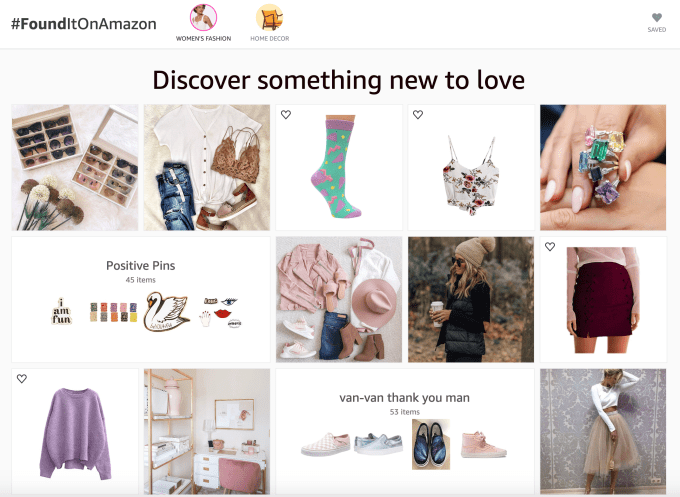
Interesting Finds has been around since 2016, offering consumers a way to browse an almost Pinterest-like board of products across a number of categories. It features curated “shops” focused on niche themes, like a “Daily Carry” shop for toteable items, a “Mid Century” shop filled with furniture and décor, a shop for “Star Wars” fans, one for someone who loves the color pink, and so on. Interesting Finds later added a layer of personalization with the introduction of a My Mix shop filled with recommendations tailored to your interactions and likes.
The Interesting Finds site had a modern, clean look-and-feel that made it a more pleasurable way to browse Amazon’s products. Products photos appeared on white backgrounds while the clutter of a traditional product detail page was removed.
We understand from people familiar with the products that Interesting Finds is not shutting down as Spark has. But the new #FoundItOnAmazon site will take inspiration from what worked with Interesting Finds and Spark to turn it into a new shopping discovery tool.
Interesting Finds covers a wide range of categories, but #FoundItOnAmazon will focus more directly on fashion and home décor. Similar to Interesting Finds, you can heart to favorites items and revisit them later.
The #FoundItOnAmazon site is very new and isn’t currently appearing for all Amazon customers at this time. If you have it, the amazon.com/spark URL will take you there.
Though Amazon won’t talk about why its Instagram experiment is ending, it’s not too hard to make some guesses. Beyond its lack of originality and transactional nature, Instagram itself has grown into a far more formidable competitor since Spark first launched.
Last fall, Instagram fully embraced its shoppable nature with the introduction of shopping features across its app that let people more easily discover products from Instagram photos. It also added a new shopping channel and in March, Instagram launched its own in-app checkout option to turn product inspiration into actual conversions. It was certainly a big move into Amazon territory. And while that led to headlines about Instagram as the future of shopping, it’s not going to upset Amazon’s overall dominance any time soon.
In addition to the shifting competitive landscape, Spark’s primary stakeholder, Amazon VP of Consumer Engagement Chee Chew departed at the beginning of 2019 for Twilio. While at Amazon, Chew was heavily invested in Spark’s success and product managers would even tie their own efforts to Spark in order to win his favor, sources said.
For example, Amazon’s notifications section had been changed to include updates from Spark. And Spark used to sit a swipe away from the main navigation menu on mobile.
Following Spark’s closure, Amazon’s navigation has once again been simplified. It’s now a clutter-free hamburger menu. Meanwhile, Amazon’s notifications section no longer includes Spark updates — only alerts about orders, shipments, and personalized recommendations.
In addition, it’s likely that Spark wasn’t well adopted. Just 10,000 Amazon customers used it during its first 24 hours, we heard. With Chew’s departure, Spark lost its driving force. No one needed to curry favor by paying it attention, which may have also helped contribute to its shuttering.
6/14/19, 10:20 PM ET: Updated with further context after publication.
This neural network detects whether faces have been Photoshopped
Using Photoshop and other image manipulation software to tweak faces in photos has become common practice, but it’s not always made clear when it’s been done. Berkeley and Adobe researchers have created a tool that not only can tell when a face has been Photoshopped, but can suggest how to undo it.
Right off the bat it must be noted that this project applies only to Photoshop manipulations, and in particular those made with the “Face Aware Liquify” feature, which allows for both subtle and major adjustments to many facial features. A universal detection tool is a long way off, but this is a start.
The researchers (among them Alexei Efros, who just appeared at our AI+Robotics event) began from the assumption that a great deal of image manipulation is performed with popular tools like Adobe’s, and as such a good place to start would be looking specifically at the manipulations possible in those tools.
They set up a script to take portrait photos and manipulate them slightly in various ways: move the eyes a bit and emphasize the smile, narrow the cheeks and nose, things like that. They then fed the originals and warped versions to the machine learning model en masse, with the hopes that it would learn to tell them apart.
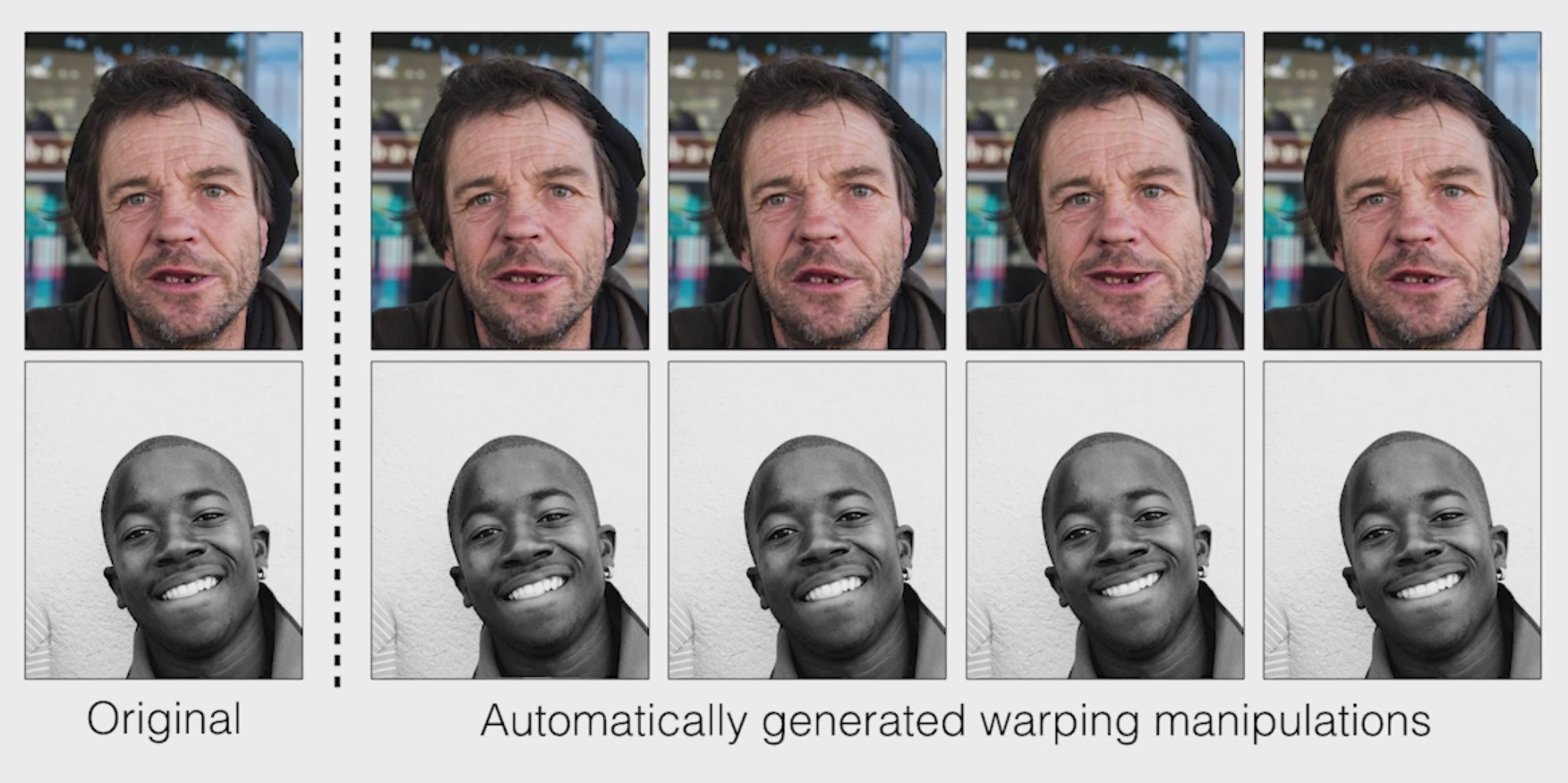 Learn it did, and quite well. When humans were presented with images and asked which had been manipulated, they performed only slightly better than chance. But the trained neural network identified the manipulated images 99 percent of the time.
Learn it did, and quite well. When humans were presented with images and asked which had been manipulated, they performed only slightly better than chance. But the trained neural network identified the manipulated images 99 percent of the time.
What is it seeing? Probably tiny patterns in the optical flow of the image that humans can’t really perceive. And those same little patterns also suggest to it what exact manipulations have been made, letting it suggest an “undo” of the manipulations even having never seen the original.
Since it’s limited to just faces tweaked by this Photoshop tool, don’t expect this research to form any significant barrier against the forces of evil lawlessly tweaking faces left and right out there. But this is just one of many small starts in the growing field of digital forensics.
“We live in a world where it’s becoming harder to trust the digital information we consume,” said Adobe’s Richard Zhang, who worked on the project, “and I look forward to further exploring this area of research.”
You can read the paper describing the project and inspect the team’s code at the project page.
Walmart Grocery is now offering a $98 per year ‘Delivery Unlimited’ subscription
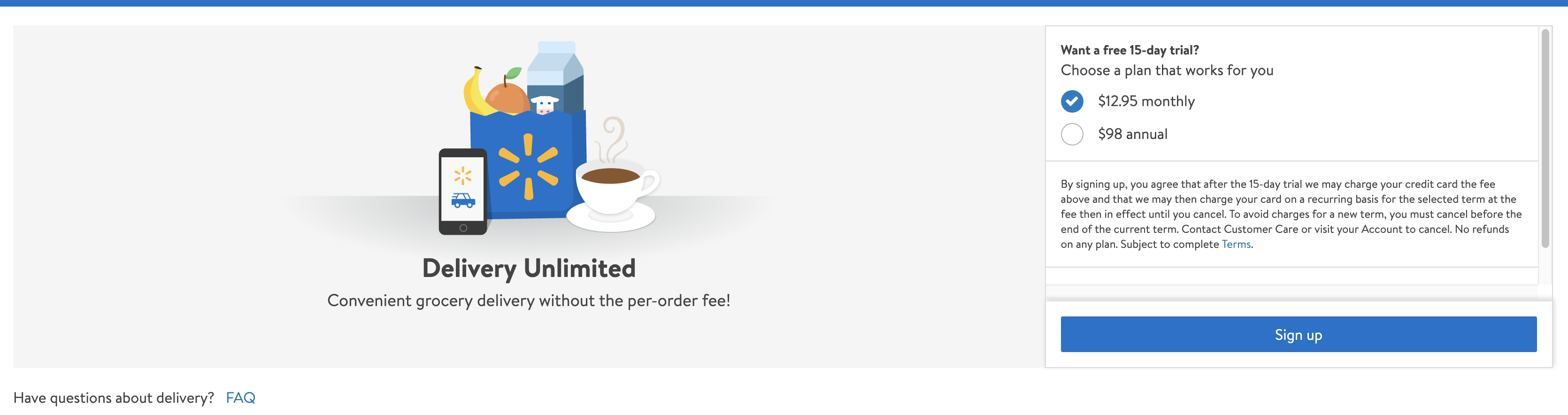
Walmart is taking aim at Instacart, Target’s Shipt and Amazon Prime Now/Whole Foods with a new grocery delivery subscription service called simply, “Delivery Unlimited.” Before, Walmart shoppers could order groceries online and pick them up at their local store for free or they could opt to pay the $9.95 (or sometimes less) per-order delivery fee. Delivery Unlimited is a third option that offers consumers a way to skip the per-order fee in favor of a monthly or annual subscription.
Currently, the retailer is offering a $12.95 per month plan or a $98 per year subscription, both of which include a 15-day trial period (see below).
Everything else about the service is the same.
You’ll still shop online or in the Walmart Grocery app, build a basket and pick a time slot for your order. There aren’t any restrictions on delivery times, either. It’s just another way to pay for your online orders — and one that could potentially save you money if you order groceries online from Walmart more than once per month.
At $98 per year, Walmart’s Delivery Unlimited service is competitively priced.
Shipt today charges $99 annually, and Target just this week announced a way for Shipt shoppers to pay a per-order fee of $9.99 for the first time, with a Shipt integration on Target.com. Instacart, meanwhile, cut its annual fee to $99 in November. Prime Now is the most expensive option at $119 per year. But of course, it includes more than just grocery delivery — Prime is a comprehensive benefits program that includes fast shipping from Amazon.com, access to streaming services, free e-books and more.
It’s unclear how broadly available Delivery Unlimited is today. The FAQ on Walmart’s website only vaguely answers a question about availability, saying that “there’s a good chance Delivery Unlimited is in your area.”
Okay!
The service is also mentioned in an Instagram post from March published by the account belonging to a single Walmart store in Utah, which is likely one of the earlier test markets.
We reached out to Walmart for details, but the retailer has yet to respond to questions about the Delivery Unlimited service, or clarify how long it’s been around.
The official Walmart Grocery FAQ makes no mention of a subscription option at this time, and there’s been no formal announcement.
Unlike some grocery delivery businesses, Walmart doesn’t operate its own network of delivery professionals or independent contractors. Instead, Walmart partners with delivery providers across the U.S., including Point Pickup, Skipcart, AxleHire, Roadie, Postmates and DoorDash. It has also tried, then ended, relationships with Deliv, Uber and Lyft.
Walmart’s heavy investments in online grocery have boosted its bottom line. Grocery, along with the growth taking place across the home and fashion categories, has helped the retailer grow its e-commerce sales. In the first quarter, e-commerce sale were up 37%, Walmart said, with earnings per share of $1.13 versus $1.02 expected, and revenue of $123.93 billion above the $125.03 billion estimated.
The retailer currently offers grocery pickup at 2,450 locations and delivery at nearly 1,000 locations. It says it’s on track to offer pickup at 3,100 stores and delivery at 1,600 by the end of 2019.
Cellebrite Now Says It Can Unlock Any iPhone for Cops
In a strangely public product announcement, the phone-cracking firm revealed a powerful new device.
Days after pledging to expand internet, Ethiopia’s government shuts it off
Days after Ethiopian ICT officials made public pledges to improve net access, the government began playing on-again, off-again with the internet — shutting it down (almost completely) to coincide with the country’s national exams.
Data provided to TechCrunch from Oracle’s Internet Intelligence confirmed intermittent net blackouts from June 11 to 14, with connectivity returning for brief periods during that time-span.
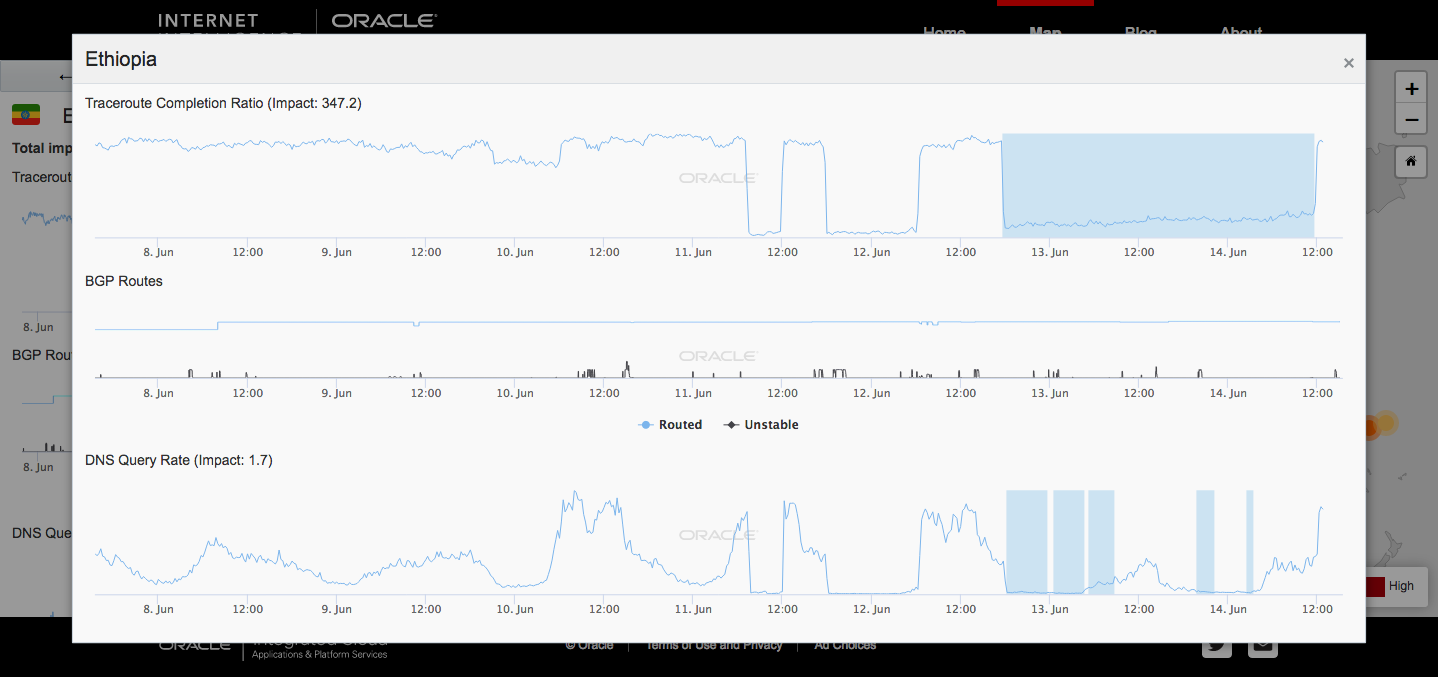
Sources on the ground, including in the country’s tech community, confirmed to TechCrunch internet stoppage over the period.
Mobile and IP connectivity in Ethiopia is managed by state-owned Ethio Telecom, though the government — led by newly elected Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed and President Sahle-Work Zewde — has committed to break up the telecom and privatize it.
On the reason for the outage, the government of Ethiopia has not issued a statement and a government official in charge of ICT policy did not respond to a TechCrunch inquiry.
Press reports, and a source speaking to TechCrunch on background, said Ethiopia’s internet stoppage was done to stop students from cheating on national exams, which took place this week.
Earlier this week I attended Ethiopia’s ICT Expo and first Startup Ethiopia event, moderating and sitting on panels with Ethiopian government representatives to discuss the country’s startup community and internet landscape. Several officials, such as State Minister of Innovation and Technology Jemal Beker, named specific commitments to improve the country’s internet quality, access and choice within the next year.
Ethiopia took policy steps in that direction, announcing steps this week to issue individual telco licences by the end of 2019.
The East African nation of 100 million with the continent’s seventh largest economy is bidding to become Africa’s next startup hub.
Ethiopia has a budding tech scene, but lags the continent’s tech standouts — like Nigeria, Kenya and South Africa — that have become focal points for startup formation, exits and VC.
Still, startups such as local ride-hail ventures Ride and ZayRide have started to gain traction (Uber has not yet entered Ethiopia). This week’s Startup Ethiopia event also showcased high-potential early-stage ventures, such as payment company YenaPay and agtech e-commerce startup Deamat.
One thing discussed at Startup Ethiopia was the need for startups — most of which operate on mobile platforms — to have consistent, affordable and accessible internet to drive forward business models.
Ethiopia is taking steps and making statements in that direction, but this week’s net stoppage shows there are still hurdles and disconnects.
One of those is the country’s government pursuing an internet shutdown just days after attempting to convince investors, angel networks and a global tech audience it’s serious about making Ethiopia an African startup hub.
From Project Scarlett to Gooigi: The best of E3 2019
Every story about E3 has opened with a mention of Sony’s absence, and this one’s no different. The lack of one of gaming’s “big three” loomed large over the show, right down to a strange sense of space on the showroom floor.
Even Xbox chief Phil Spencer mourned the absence of the company’s biggest competitor, stating, “I wish Sony was here,” during a live stream.
But the show went on, as it has through countless ebbs and flows of the gaming industry. Sony’s clearly got plenty up its sleeve with regard to next-generation content, and frankly, no one’s too worried about their health.
Microsoft, meanwhile, came out swinging on Sunday. The company had a TON of games to reveal at the show, with dozens of trailers, all told. And while Microsoft did touch upon two key pieces of news, it ultimately ended up blowing through those announcements, with very little time devoted to either its next-generation 8K console, Project Scarlett, or its streaming service, Project xCloud.
In fact, we ultimately went back to Microsoft later in the week to clarify some things about the service and discovered in the process that console streaming will be free and not a part of the broader xCloud offering.
While Microsoft ultimately seemed cautious (or pressed for time) to go into either xCloud or Game Pass in too much detail onstage, streaming was unquestionably the biggest story of the show. That’s due in no small part to the fact that Google took a little wind out of E3’s sails by shedding more light on its Stadia offering during a surprise press conference last Friday.
On Tuesday, a Nintendo executive confirmed for me that the company is exploring streaming, but wasn’t able to comment on any specifics. Regardless, the writing is clearly on the wall here, and Nintendo has certainly taken notice. In the meantime, the company showed off its latest Animal Crossing title, a sneak peek of the next Zelda and the surprise hit of the show: A gooey Luigi called, naturally, Gooigi. Honestly though, I’m most excited about that Link’s Awakening remaster.
Square’s big event was fairly lackluster, though we did get a preview of the Uncanny (Valley) Avengers. Ubisoft had some cool demos on tap, including Watch Dogs: Legion and story mode for Assassin’s Creed. The publisher is also launching its own streaming service, with help from Google Stadia. Bethesda, meanwhile, is getting in on the battle royale phenomenon with a new mode for Fallout 76. Though the Fall Guys’ version is far more adorable.
There’s a Razer energy drink, Opera gaming browser, new George R.R. Martin game, Warcraft-meets-The-Office show from the It’s Always Sunny crew and a dance game for the Nintendo Wii. Not the Switch, not the Wii U, the Wii. Happy E3 2019!
ThinkGeek.com to close, replaced as a section of GameStop
Sad news for anyone who loves geeky goods and top-notch April Fools’ jokes: ThinkGeek.com, the 20-year-old online retailer known for selling more geek-centric gadgets and peripherals than you could fit in a TARDIS, is going away.
According to an FAQ sitting at the top of its site, ThinkGeek isn’t “shutting down,” it just won’t continue on as the site we’ve come to know, instead living on as a shadow of its former self as a section in GameStop (which acquired ThinkGeek in 2015 for a reported $140 million.)
Says the FAQ:
On July 2nd, 2019, ThinkGeek.com will be moving in with our parent company GameStop. After this move, you will be able to shop a curated selection of unique items historically found on ThinkGeek.com via a ThinkGeek section at GameStop
The word “curated” is pretty key, there, because there’s just no way a couple of shelves in GameStop will be able to cover the array of fandoms that ThinkGeek.com covered. From Marvel, to Star Wars, to Potter, to Tolkien, it covered a whole lot of (fan)bases in one swoop.
ThinkGeek.com is — or, I guess, was — one of those shops that was fun to explore; anytime I found myself there, I’d inevitably lose track of time clicking around from category to category, often throwing down a credit card for some Star Wars shirt or Aperture Science pint glass I probably didn’t need. Hopefully that sense of “Oooh, look at that! And that! And that!” will live on in whatever section springs up on GameStop’s site.
The company also says that the 40 standalone ThinkGeek retail stores dotting the U.S. will stay open.
This news comes after a few back-to-back 75%-off sales of all clearance goods, and now it looks like they’ve marked things down 50% site-wide to clear the warehouses.
Perhaps most of all, we’ll miss ThinkGeek’s April Fools’ day gags. On a day in which many companies find themselves trying a bit too hard to make us laugh, ThinkGeek just always seemed to get it right. They’d sprinkle their site with fake product listings for people to stumble upon. Things like…
The Fortnite R/C Battle Bus:

Or the Admiral Ackbar Singing Bass:

Or the absolutely brilliant Tauntaun sleeping bag (a gag that proved so popular that they ended up making and selling them for a while):

Alas.
ThinkGeek says it’ll still take return requests for orders made before June 13th, and that any ThinkGeek gift cards you’ve got sitting around will be honored at GameStop’s online and real-world locations.
NASA asks private companies to share how they might supply the Lunar Gateway
NASA’s stated goal of sending the first woman ever, and the first man since the Apollo program, to the Moon involves setting up a new space station that will orbit the Moon, which is supposed to begin being built by the end of 2022, per current timelines. Today, the U.S. space agency issued an open call for industry feedback and insight on how American companies might help supply said station.
Like the ISS, the forthcoming “Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway” (aka the LOP-G, but much more commonly simply referred to as “The Gateway”) will need regular resupply runs and delivery of cargo — both for the many stages of its build, which are projected to span at least six years to get to its target state of completion. NASA is also considering the possibility that private companies could provide transportation for parts of its lunar landing and, eventually, exploration and base building on the Moon.
NASA’s move today is to release a draft request for proposals, which means that at this stage, it’s not actually looking for providers to submit formal bids — this is the step before that happens, when it’s more informally looking for guidance from industry on what kinds of cargo delivery methods they might even be able to provide ahead of looking to lock in any official contract winners for ongoing business.
To dive deeper into what it’s after and field questions from industry, NASA is hosting a Q&A on June 26, and comments are due on July 10. The more formal actual RFP will happen later this summer, the agency expects, and ultimately, the contract award for this admittedly big job could be as high as $7 billion.
NASA previously awarded private official “Commercial Resupply Services” for the ISS, which is a similar type of business but much closer to home, to SpaceX and Orbital Sciences, and then another round of CRS contracts more recently to Orbital ATK (the new Northrop Grumman-owned entity which Orbital Sciences became), Sierra Nevada and SpaceX once again. It’s likely SpaceX will once again bid, as could Blue Origin, Northrup Grumman and Lockheed Martin, to name a few.
Price tag to return to the Moon could be $30 billion
NASA’s ambitious plan to return to the moon may cost as much as $30 billion over the next five years, the agency’s administrator, Jim Bridenstine, indicated in an interview this week. This is only a ballpark figure, but it’s the first all-inclusive one we’ve seen and, despite being a large amount of money, is lower than some might have guessed.
Bridenstine floated the figure in an interview with CNN, suggesting that the agency would need somewhere between $20 billion and $30 billion for the purpose of returning to the surface of the Moon. Anything beyond that, such as fleshing out the Lunar Gateway or establishing a persistent presence, would incur additional costs.
To put this figure in perspective, NASA’s annual budget is about $20 billion, very little compared to many other agencies and budget items in the federal government. The speculated additional costs would average $4-6 billion per year, though spending may not be so consistent. NASA only asked for an additional $1.6 billion for the upcoming year, for instance.
The idea that this return to the Moon could cost the same in 2019 dollars as Apollo cost in 1960s dollars (about $30 billion) may be surprising to some. But of course we are not inventing crewed interplanetary travel from scratch this time around. Billions have already been invested in the technologies and infrastructure underpinning the Artemis mission, both flight-proven and recently developed.
In addition to that, Bridenstine is likely counting on the cost savings NASA will see by partnering with commercial aerospace concerns far more extensively than in previous missions of this scale. Cost-sharing, co-development and use of commercial services rather than internal ones will likely save billions.
A secondary goal, Bridenstine told CNN, was “to make sure that we’re not cannibalizing parts of NASA to fund the Artemis program.” So sucking money out of other missions, or co-opting tech or parts from other projects, isn’t an option.
Whether Congress will approve the money is an open question. More concerning is the fundamental timeline of technology development and deployment over the next five years. Even with billions at its disposal, NASA may find that a mission to the lunar surface simply isn’t feasible to complete in that duration, even if all goes according to plan. The SLS and Orion projects are over budget and have been repeatedly delayed, for instance.
Ambition and aggressive timelines are part of NASA’s DNA, however, and although they can plan for the best, you better believe their engineers and program managers are preparing for the worst as well. We’ll get there when we get there.
Hackers Target US Power, Amazon Clones a Neighborhood, and More News
Catch up on the most important news from today in two minutes or less.
