#ADayOffTwitch and dozens of subreddit blackouts were organized separately, but together they show the potential power of collective action by users.
Category: Tech news
hacking,system security,protection against hackers,tech-news,gadgets,gaming
The Best Turntables for Your Vinyl Collection
Looking for fresh indoor hobbies? Why not start a record collection? These entry-level turntables will help you enjoy analog audio at home.
The Case for Video Game Tutorials
They might not all be perfect, but they’ve become necessary.
They Watched a YouTuber With Tourette’s—Then Adopted His Tics
Hundreds of people are displaying similar behaviors to that of YouTube star Jan Zimmermann. Do they have a disorder or something more mysterious?
Coral Capital closes third fund with $128M for startups in Japan
Coral Capital, a Tokyo-based venture capital firm, announced today that it has closed its third fund, Coral Capital III, raising $128 million (14 billion yen). Coral Capital’s total assets under management (AUM) is now $275 million.
Limited partners in the vehicle include Mizuho Bank, Mitsubishi Estate, Shinsei Bank, Pavilion Capital, Founders Fund, Dai-ichi Life Insurance, GREE, and undisclosed domestic and international institutional investors.
Coral Capital, founded by two partners James Riney and Yohei Sawayama, will continue to invest in seed and early-stage companies in Japan, deploying first checks from $500,000 to $5 million, and follow-on funding, CEO and founding partner Riney told TechCrunch.
“We have made a few large follow-on investments – $20 million into SmartHR and $17 million into Graffer. we also allocated a significant portion of our latest fund for follow-on investment,” Riney said. About 30% of its third fund is from global investors including the US, Asia and Europe, and Coral Capital wants to be a bridge between its Japan-based portfolio companies and global venture capital community for reaching international scale, Riney continued.
What makes the latest fund unique is that it has a longer fund life that can be extended to 14 years, Riney said. “We want our founders to focus on building without the pressure of a VC looking for a quick exit,” Riney told TechCrunch. Its previous two funds had about 10 years of fund life, Riney noted.
Riney and Sawayama, who were co-founders of 500 Startups Japan, launched their first fund in partnership with 500 Startups in February 2016. Coral Capital has set up its $45 million second fund, Capital Fund II under their own brand name, in February 2019.
Coral Capital has invested in over 80 companies in Japan and exited 7 companies so far, according to Riney. It has made a raft of investments including SmartHR, Graffer, GITAI, and Kyoto Fusioneering.
The company will focus on investing digital transformation in areas including SaaS, insurance, fintech, healthcare, deep tech, fusion engineering companies, robotic companies, Riney told TechCrunch.
The Japanese startup ecosystem is striking its stride now compared to 9 years ago, Riney said. As Riney and Sawayama started investing in seed and early-stage startup companies back in 2012, the startup world was a black box in the country, according to Riney. There was less than a billion invested into startups every year and hardly any unicorns in Japan, and there was not enough information available in Japanese on building companies, he said.
Many startups in Japan are now forgoing an early IPO and raising larger amounts in later stage rounds, Riney said.
Japan’s annual startup investment is estimated at $5 billion, with six unicorns including Coral Capital’s portfolio company, up from just about $600 million in 2012. The $5 billion in annual startup investment is nothing when you consider that the U.S. and China attract tens of billions, and even neighboring country Korea attracts about $4 billion and produced Coupang, a decacorn, Riney said. “We can do better, and we will” and Coral Capital will continue to support and play an important role in driving the ecosystem forward in Japan, Riney added.
Coral Capital also plans to double down on its media outlet, Coral Insights, and recruit staff for building its community. Many startup founders, employees, and investors publish content on their learnings, raising the bar for everyone in the ecosystem and Japan is starting to look a lot more like Silicon Valley, Riney said.
Southeast Asia “omnichannel” health startup Doctor Anywhere gets $88M SGD
Doctor Anywhere, a startup that takes an “omnichannel” approach to healthcare, announced today it has raised $88 million SGD (about $65.7 million USD) in Series C funding. The round was led by Asia Partners, with participation from Novo Holdings, Philips and OSK-SBI Partners. It also included returning investors EDBI, Square Peg, IHH Healthcare, Kamet Capital and Pavilion Capital.
As part of the round, Asia Partners co-founder Oliver Rippel and Novo Holdings Equity Asia senior partner Dr. Amit Kakar will join Doctor Anywhere’s board of directors. The company’s Series C, which it claims is one of the largest private rounds raised by a Southeast Asian healthtech company, brings its total funding to more than $140 million SGD.
Doctor Anywhere’s omnichannel approach means that in addition to online consultations, it runs in-person clinics, provides home visits, medication deliveries and operates an in-app marketplace for health and wellness products.
Founded in 2017 by Lim Wai Mun, Doctor Anywhere claims it now serves more than 1.5 million users. It is available in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam and the Philippines, and recently established tech hubs in Bangalore and Ho Chi Minh City.
Lim told TechCrunch in an email that when he started working on Doctor Anywhere, there were already successful telemedicine platforms in the United States, the United Kingdom and China, but the model was still nascent in Southeast Asia. A former investor, Lim began Doctor Anywhere as a side project because he had older relatives who could not leave their homes for medical visits.
Doctor Anywhere launched as an online-only telehealth platform, but “we quickly realized that physical presence is very important in order to build trust with users,” Lim said. As a result, the company started its home care services and physical clinics.
According to Doctor Anywhere’s estimates, the COVID-19 pandemic fast-tracked the adoption of telehealth services in Southeast Asia by at least five years. The company saw more demand for online medical consultations, medication deliveries and marketplace purchases.
“In the past year, we have more than doubled the size of our network, from around 1,000 providers at the start of 2020 to currently close to 2,500 medical professionals across Southeast Asia,” Lim said.
In response to the pandemic, Doctor Anywhere launched an online COVID-19 Medical Advisory Clinic last year to provide on-demand consultations for people with suspected symptoms. It also created an online mental wellness module with psychologists. Lim said the company has seen an increase in demand for mental health-related services, like insomnia and anxiety.
Other telehealth startups in the region include WhiteCoat, Speedoc and Doctor World. Lim said Doctor Anywhere wants to differentiate by quickly launching new products in response to user inquiries, and “cultivating a balance between technology and human touch.”
The funding will be used to deepen Doctor Anywhere’s presence in its current markets and expand into new ones. It also plans to scale its tech infrastructure and big data capabilities for a better online-to-offline user experience, and will introduce new medical specialty modules, shorten medication delivery times and develop personalized healthcare plans.
Rugged showcases its layout-printing construction robots
Few robotics categories are poised to benefit more from the events of the past year than construction. It’s a booming field that could benefit massively from automaton, a fact that’s only been amplified as the pandemic brought many nonessential businesses to a standstill. We’ve seen a number of players in the category raise notable rounds over the past year or so, including Toggle, Dusty, Scaled and SkyMul.
Founded in 2018, Houston-based Rugged Robotics raised a $2.5 million seed round back in 2019. While the company isn’t actively raising at the moment, it has already begun to roll out its technology in early pilots, including a partnership with Massachusetts-based construction-firm Consigli.

Image Credits: Rugged Robotics
“We had a client that was pretty progressive looking,” said Consigli’s Jack Moran. “It’s a building where we were controlling the core shell of the project, as well as the fit-out, which was pretty complex — lots of odd shapes that would be a challenge for us.”
Rugged’s self-described “layout Roomba” was used to help build a 10-story building in Cambridge, Massachusetts, effectively drawing blueprints on the ground of the space that amounted to around 40,000 square feet per floor. The partnership effectively finds Rugged taking a key step from its early research and development mode to commercialize.
“The layout process is the most important task in the construction process,” Rugged founder and CEO Derrick Morse said in an interview with TechCrunch. “Marking where things are installed defines where things are built. A mistake made during layout trickles into the overall construction process and it results in rework, delays and additional expenses.”
The team is still small, with a headcount of around six full-time employees, including co-founders with backgrounds at NASA and Samsung. The team currently has three robots, with plans to expand to five. They print dot matrix ink patterns on the ground to give construction teams a real-world orientation for the buildings they’re creating.

Image Credits: Rugged Robotics
A member of the Rugged team travels to the site with the robot to supervise the robot as it executes on its plans, with the startup charging the construction company through a RaaS (robotics as a service) model.
“We have insatiable customer demand,” said Morse. “We have several multibillion-dollar contractors that are excited to do pilots and demos with us. We’ll be growing the organization and fleet in the upcoming 12 months, and we’ll likely be bringing in additional capital to enable that growth.”
Daily Crunch: China sets three-hour weekly time limit for under-18 gamers
To get a roundup of TechCrunch’s biggest and most important stories delivered to your inbox every day at 3 p.m. PDT, subscribe here.
Hello and welcome to Daily Crunch for August 30, 2021. The startup world is gearing up for Y Combinator Demo Day this week, but the rest of tech isn’t taking a pause. So we have Apple news, Telegram news, antitrust news, video game news, you name it.
But we have some TechCrunch news to start: Ryan Reynolds is coming to Disrupt to talk about his company, Maximum Effort. That’s pretty hype. And we’re going to be talking about software. A lot. — Alex
The TechCrunch Top 3
- China restricts youth gaming: To three hours per week! Which isn’t much! For a country with a large games market like China, this is big darn news. But it’s just one part of a larger regulatory push in China (including things as far afield as taking on online fan culture!) to bring its private companies more in line with the government’s plans.
- Toast’s IPO looks tasty: TechCrunch took a longer look at Boston-based Toast’s IPO filing today. Our takeaways? That the company has posted admirable growth since its COVID lows and has a very sturdy multipart business model. The company is doing the very active Boston startup scene proud.
- Spotify buys Joe Rogan, Apple buys classical music? The campaign to build differentiated music streaming services in an era when music is available everywhere hotted up this week with Apple buying Primephonic. The smaller company, based in Amsterdam, will be absorbed into Apple Music.
Startups/VC
Ready for a broadside of startup news? Good. We have what you need. But first, as a sign of the times, Telegram just crossed the 1 billion download mark. That’s an achievement, sure, but also goes to show that maybe consumers do care about privacy after all.
- Casper’s unfriendly ghost fails to haunt Eight Sleep: Remember when D2C mattress company Casper went public, and it went poorly? That misstep has not stopped investors from putting new capital into Eight Sleep, which makes smart mattresses. The startup just raised $86 million in a Series C round of funding that values it at nearly a half-billion dollars.
- Prive raises $1.7M for better e-commerce subscriptions: Two ex-Uber folks are building something new to make e-commerce subscriptions, helping both retailers sell more goods and consumers get better recommendations. Win/win.
- At long last, a personal CRM? I don’t want to get your hopes up, as building a personal CRM has been a white whale in startupland for some time. But Clay, a startup that just raised $8 million, has put together what TechCrunch calls “a system designed to help you be more thoughtful with the people in your life.” Please let it be good. I need help.
- Alpaca proves that embedded fintech is still hot: TechCrunch has covered Alpaca a few times in recent years, both when it raised capital and when we were delving more deeply into the world of API-delivered startups. Today the company announced a $50 million Series B, a partnership with Plaid and support for crypto trading. Alpaca’s work to provide other fintechs with embedded equities trading appears to be going well.
- How does one become a travel influencer? I don’t know. But if you become one, Thatch wants you to be able to better monetize your recommendations. If you are currently a travel influencer, this is good news. If you were hoping that influencers would lose influence in the coming years, this is not.
- To cap us off today, Ola Electric is looking to raise between $250 million and $500 million. That’s a huge chunk of change. The deal has yet to close, but our early reporting indicates that Ola’s electric vehicle business is about to be more than flush. “Falcon Edge Capital is in advanced talks to lead the round, which values Ola Electric between $2.75 billion to $3.5 billion,” TechCrunch reports.
- Plus, over the weekend I wrote about why startups are going to win the battle to set the tone regarding remote work, in case you wanted to give that a read.
How Amazon EC2 grew from a notion into a foundational element of cloud computing
In August 2006, AWS activated its EC2 cloud-based virtual computer, a milestone in the cloud infrastructure giant’s development.
“You really can’t overstate what Amazon was able to accomplish,” writes enterprise reporter Ron Miller.
In the 15 years since, EC2 has enabled clients of any size to test and run their own applications on AWS’ virtual machines.
To learn more about a fundamental technological shift that “would help fuel a whole generation of startups,” Ron interviewed EC2 VP Dave Brown, who built and led the Amazon EC2 front-end team.
(Extra Crunch is our membership program, which helps founders and startup teams get ahead. You can sign up here.)
Big Tech Inc.
- ByteDance buys VR hardware startup: Sure, Facebook is a leader in the VR hardware game, but it’s hardly the only player. TikTok parent company ByteDance is looking to take Facebook on by buying Pico, which had raised a $37 million round earlier this year. It’s not clear how this news intersects with gaming restrictions in China, but now we should have national champions duking it out in the VR market.
- Instagram wants to know your birthday: If you aren’t into giving Facebook products more of your data, bad news today from Instagram. It will prompt users to share their birthday and only allow so many deferrals. Why? TechCrunch reports that the change is to help “personalize your experience” on the service. Which means ads.
- Ideanomics buys Via Motors: Ideanomics, a public mobility company, is spending $450 million in stock to buy Via Motors, an EV company. Shares of Ideanomics are up just over 5% today on the news.
- It turns out that most Big Tech employees aren’t opposed to antitrust enforcement, even though the ideas being bandied about the halls of Congress could make life harder for the megacorps that currently constitute the top end of the technology industry.
TechCrunch Experts: Growth Marketing

Image Credits: SEAN GLADWELL (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Are you all caught up on last week’s coverage of growth marketing? If not, read it here.
TechCrunch wants you to recommend growth marketers who have expertise in SEO, social, content writing and more! If you’re a growth marketer, pass this survey along to your clients; we’d like to hear about why they loved working with you.
Community
 Image Credits: Diversion Books
Image Credits: Diversion Books
Join Danny Crichton on Twitter Spaces tomorrow, Tuesday, August 31st at 1 p.m. PDT/4 p.m. EDT as he talks with Azeem Azhar about his upcoming book, “The Exponential Age: How Accelerating Technology is Transforming Business, Politics and Society,” which will be released on September 7, 2021.
Square to launch a new paid subscription, Invoices Plus
Square’s popular free invoicing software is becoming the company’s next big subscription service. The company is poised to announce a paid subscription offering called Invoices Plus, which will offer sellers a set of advanced features, including some that had previously been available with the free service. The service itself had been quietly introduced to individual sellers, but has not yet been publicly announced.
Some sellers who were already using Square Invoices were recently alerted to the upcoming changes via email.
In the announcement shared with some sellers (the details of which can also be viewed here on a Square Seller Community forum), the new subscription will include a series of features that were released in the past year as part of a limited trial.
This includes multi-package estimates, custom invoice templates and custom invoice fields. These will now become a part of Invoices Plus, as will two other features: the ability to automatically convert accepted estimates to invoices and the ability to build milestone-based schedules (three-plus installment invoices). Square’s announcement said it will introduce a “trial” button next to these features in the Square Invoices software to alert customers to the upcoming capabilities (see below).

Image Credits: Square website
Square’s free invoicing software will not go away, the announcement noted. Sellers will be able to send unlimited invoices for free, as well as estimates and contracts, with the free plan. Free users will also be able to use invoice tracking, reminders and reporting tools.
The free plan has historically relied on processing fees to generate revenue. At present, this is 2.9% + $0.30 per invoice paid online by check or debit card plus a 1% fee per ACH transaction, per Square’s website. (Fees are slightly lower on in-person transactions and slightly higher for “card on file” transactions.) Pricing for the new, paid subscription has not yet been publicly announced.
A Square employee had explained the reasoning behind the change on the community forum site. They noted that many of Square’s other products — like Square Online, Appointments, Square for Retail and Square for Restaurants — also offer both a free and paid tier. And although Square charges processing fees for Square Invoices, they aren’t enough to fuel its product development. With Invoices Plus, they said, the company aims to compete more directly with paid invoicing apps and products and the more advanced features those products offer.
Reached for comment, Square confirmed to TechCrunch Invoices Plus is a software subscription the company plans to announce shortly. But the company didn’t want to share more details until the news is official.
References to the new subscription have also already made their way to the Square app’s code, where they were spotted by iOS developer Steve Moser. The code indicates users who previously used some of the paid-only features will be able to still use them for the time being. But as the announcement also noted, sellers would not be able to use the paid features for free the next time they’re creating new files with Square Invoices.
Image Credits: Steve Moser
The new service arrived shortly after Square announced earnings, where it noted its seller business brought in $1.31 billion in revenue (out of the total of $4.68 billion) and $585 million of gross profit in the second quarter, driven in part by continued strong online growth. The company also announced its plan to acquire the buy now, pay later giant Afterpay in a $29 billion deal, speaking to its interest in chasing the broader payments market. The deal also offers Square a way to connect its different products by allowing Afterpay customers to pay their monthly installments through Square’s Cash App, the company said.
An integration between Square and Afterpay is something that could be seen further down the road, as well, one could imagine. That’s something Square also hinted toward in a response to another seller on its community forum site, where a rep updated an older answer to share news of the acquisition, adding Square didn’t “have integration timelines to share at the moment.”
New Zealand-based student well-being platform Komodo raises $1.8M NZD
Adolescence is a turbulent period and its challenges are being exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Even in the best of times, teens dealing with personal and school problems might have trouble talking about them. New Zealand-based startup Komodo is a student well-being platform that wants to give students a place to communicate with staff, while providing schools with data to help them spot and address issues like depression or bullying.
Founded in 2018 by Chris Bacon, Matt Goodson and Jack Wood, the startup announced today it has raised $1.8 million NZD (about $1.26 million) in seed funding led by Folklore Ventures, with participation from Icehouse Ventures and Flying Fox Ventures. Individual investors included employee engagement platform Culture Amp co-founder Rod Hamilton; Chloe Hamman, Culture Amp’s director of people science; leaders from learning platform Education Perfect; and Kristi Grant, the director of people experience at Auror.
Some of Komodo’s clients and partners in New Zealand and Australia include Marist College Ashgrove in Queensland; St. Andrew’s College in Christchurch; the Australian Boarding Schools Association (ABSA); Independent Schools of New Zealand; and the Council of British International Schools.
Komodo was originally created to monitor the well-being of youth athletes, based on research Bacon performed while earning a Ph.D. at the University of Canterbury. A lot of its clients were schools, and that’s when the team began to expand Komodo’s scope.
“The draw for us was witnessing specific examples,” Wood told TechCrunch. “We had schools coming back to us saying ‘we’ve got a kid that’s been bullied for the past three months who hasn’t even remotely felt confident to approach a staff member and start talking about it. We’ve finally seen that come up in Komodo and they feel happy they have a confidential channel to voice that concern.’”

Komodo co-founders Jack Wood and Chris Bacon. Image Credits: Komodo
Komodo has a web application and a mobile app, which is what most students use. The platform can be customized by schools and includes psychologist-designed surveys and questions about topics like how students feel about going to school, socialization and relationships or major transitions like starting high school or preparing for university. The amount of time students check into Komodo depends on their school. At some it’s once a week, others once every two weeks or month. Schools use the platform differently based on their environment — for example, if they’re learning remotely, they may do more frequent check-ins.
For schools, data collected from surveys can help them see trends emerge and catch potential problems earlier, like cyberbullying. Before implementing Komodo, its founders say some schools did well-being surveys a few times per year, but many of them relied on staff and teachers’ intuition — for example, if a student who is typically outgoing suddenly becomes withdrawn. Komodo gives them a more efficient way to identify and address issues, though Wood and Bacon emphasize that it’s not meant to replace person-to-person interactions.
“Ultimately our bigger vision is facilitating and getting well-being support to students as early as possible,” said Bacon. The founders have spent a lot of time talking with Culture Amp’s Hamilton “about how it’s really important that the individuals you’re providing data to can actually understand and use it on a regular basis,” he added. “The key part for us [is] to provide visibility and psychologists who can come in and support [school staff] even more.”
Komodo’s seed funding will be used to add more psychologists to its in-house team, develop the platform and expand into more schools in Australia and New Zealand before other markets, including the United States.
Foreign investors have a bigger role to play in growing Latin America’s startup ecosystem
Contributor
There has been significant hype around Latin America’s startup success. For good reason, too: Startups have raised $9.3 billion in just the first half of 2021, almost double the amount in all of 2020, and mega-rounds are a growing trend.
But while the industry hails the rise of the region’s ecosystem and its growing fleet of unicorns, Latin America’s startup story has a far longer past. And it’s one we should keep in mind as entrepreneurs and investors around the world forge the region’s future.
People often ask me: How are consumers different in Brazil? How does the Peruvian market behave compared to the United States? These questions don’t really see each country for its inherent value, but instead gear people up to expect the unexpected from a historically economically disadvantaged region.
In fact, the evolution of business shares far more similarities across countries than we might expect. Latin America’s market has evolved over a very long time — as long as Silicon Valley and any other hub. This region has a global outlook, spectacular universities, a diverse population and an army of entrepreneurs.
It’s important for investors outside of Latin America to get involved in fundraising at earlier stages, when founders need extra support from everyone around.
That’s why the unicorns and megadeals should come as no surprise: They’re the natural evolution of the ecosystem, of more capital generating more success after years of hard work.
As Latin America has grown, competition has grown even more intense in the United States. VCs have more money than ever, and it’s getting increasingly expensive to invest in North America. So they’re looking to diversify their investments with high-potential opportunities abroad. Big funds are now dedicating resources to exclusively targeting Latin America, from SoftBank creating a region-specific fund, to Sequoia saying it will pay more attention to the region.
These incoming investors must bring more than money to ensure that entrepreneurship continues to grow in a healthy manner, rather than set it off balance. Investors should bring a local strategy that makes them an asset to Latin America’s startup ecosystem.
Investors should look for younger markets
Most Latin American companies reaching unicorn status and going public now were started around 2012. This is not very different from the timeline of businesses in other markets such as the United States. For instance, e-commerce giant MercadoLibre launched in Argentina around the time eBay was emerging.
What this tells us is that foreign investors would do well to keep a sharp eye on emerging opportunities beyond heavily covered markets like Brazil and Mexico. There is a huge opportunity to do what local investors did in Brazil and Mexico years ago, and play a significant role in the next chapter of countries with blossoming markets like Colombia, Peru or Uruguay.
U.S. investors remain shy
The amount of VC capital being funneled into Latin American startups has surged since 2017, with angel investment close behind. However, much of this investment comes from local and regional investors. Every top university in Brazil has a pool of angels. Investors in the Andean region cover Peru, Chile and Colombia. If today’s ecosystem is flourishing, it’s largely because native investors are lighting the spark.
Meanwhile, U.S. investor presence at the early stages is still low and risk averse. It’s much harder for a pre-seed or seed startup to get foreign investor interest than when they’ve already reached Series A or B. Investors also tend to come in on an ad hoc basis or as outliers brought about by a mutual contact. Foreign investors are the exception, not the rule.
It’s important for investors outside of Latin America to get involved in fundraising at earlier stages, when founders need extra support from everyone around. Investors should be pursuing a long-term strategy that will bring more consistency to the local ecosystem as a whole.
Money is not enough, investors should bring dedicated resources
Your contribution as an investor is largely about the resources you can offer. That’s especially challenging for a foreigner who has less of an understanding of the local industry and lacks a network and people on the ground.
While investors may say their your regular value offering is enough — network and U.S. customers — in truth, this won’t necessarily be of much use. Your hiring network might not be ideal for a Latin American company, and your thorough understanding of the U.S. market might not reflect developments in Latin America.
Remember that the region has a plethora of VC organizations who have worked with local startups over the course of a decade. Latin America is a very welcoming and open market, and local investors and accelerators will happily work with foreign investors, including in deal-sharing opportunities.
It’s crucial to create incentives within the ecosystem, which — like in the United States — largely means matching founders with unique opportunities. In North America, this often happens organically, because people are on the ground and actively engaged with what’s happening in the region, from networking events, to awards, and grants and partnership opportunities.
To create this in Latin America, foreign investors need to dedicate a team and money to their regional commitments. They will have to understand the local industry and be available to mentor founders with diverse perspectives.
In my experience helping EA, Pinterest and Facebook land in Latin America, we always had someone on the ground or working remotely but fully dedicated to the region. We had people focused on localizing the product, and we had research teams studying similarities and differences in user behavior. That’s how corporations land their products; it’s how VCs should land their money.
Only disrupt when it adds value
The idea is for foreign investors to strike a balance locally while creating disruptions when it helps startups look outward rather than attempting to overhaul steady, positive internal growth. That can mean encouraging companies to incorporate in the United States to make it easier for investors from anywhere to invest or preparing the company to go global. Local investors can help investors new to the region understand the balance of things that should or shouldn’t be disrupted.
Don’t be surprised when Latin America’s apparent “boom” starts happening in other emerging markets like Africa and Asia. This isn’t about a secret hack coming in from the outside. It’s just about creating the right environment for local talent to flourish and ensuring it maintains healthy growth.
Zoom announces first startups receiving funding from $100M investment fund
For more than a year now, Zoom has been on a mission to transform from an application into a platform. To that end it made three announcements last year: Zoom Apps development tools, the Zoom Apps marketplace and a $100 million development fund to invest in some of the more promising startups building tools on top of their platform. Today, at the closing bell, the company announced it has made its first round of investments.
Ross Mayfield, product lead for Zoom Apps and integrations, spoke to TechCrunch about the round of investments. “We’re in the process of creating this ecosystem. We felt it important, particularly to focus on the seed stage and A stage of partnering with entrepreneurs to create great things on this platform. And I think what you see in the first batch of more than a dozen investments is representative of something that’s going to be a significant ongoing undertaking,” he explained.
He said while they aren’t announcing exact investment amounts, they are writing checks for between $250,000 and $2.5 million. They are teaming with other investment partners, rather than leading the rounds, but that doesn’t mean they aren’t working with these startups using internal resources for advice and executive backing, beyond the money.
“Every one of these investments has an executive or senior sponsor within the company. So there’s another person inside that knows the lay of the land, can help them advance and spend more personal time with them,” Mayfield said.
The company is also running several Zoom chat channels for the startups receiving investments to learn from one another and the Zoom Apps team. “We have a shared chat channel between the startup and my team. We have a channel called Announcements and a channel called Help, and another one that the startups created called Community,” he said.
Every week they use these channels to hold a developer office hour, a business office hour (which Mayfield runs) and a community hour, where the startups can gather and talk amongst themselves about whatever they want.
Among the specific categories receiving funding are collaboration and productivity, community and charity, DE&I and PeopleOps, and gaming and entertainment. In the collaboration and productivity category, Warmly is a sales tool that provides background and information about each person participating in the meeting ahead of time, while allowing the meeting organizer to create customized Zoom backgrounds for each event.
Another is Fathom, which alleviates the need to take notes during a meeting, but it’s more than recording and transcription. “It gives you this really simple interface where you can just tag moments. And then, as a result you have this transcript of the video recording, and you can click on those tagged moments as highlights, and then share a clip of the meeting highlights to Salesforce, Slack and other tools,” Mayfield said.
Pledge enables individuals or organizations to request and collect donations inside a Zoom meeting instantly, and Canvas is a hiring and interview tool that helps companies build diverse teams with data that helps them set and meet DEI goals.
These and the other companies represent the first tranche of investments from this fund, and Mayfield says the company intends to continue looking for startups using the Zoom platform to build their startup or integrate with Zoom.
He says that every company starts as a feature, then becomes a product and then aspires to be a line of products. The trick is getting there. The goal of the investment program and the entire set of Zoom Apps tools is about helping these companies take the first step.
“The art of being an entrepreneur is working with that risk in the absence of resources and pushing at the frontier of what you know.” Zoom is trying to be a role model, a mentor and an investor on that journey.
Prive has raised $1.7 million to build a more configurable e-commerce subscription platform
Prive, a months-old, San Francisco-based startup founded by two former Uber product managers, just raised $1.7 million in pre-seed funding to create what it describes as a far more customizable e-commerce subscriptions platform for D2C brands.
The round was co-led by Patrick Chung and Brandon Farwell at XFund and Ben Ling from Bling Capital, with participation from Defy Partners, Halogen Ventures and Uber executives.
Founded by Claudia Laurie and Alex Craciun — who both spent two-and-a-half years at Uber and decided, based on their learnings about pricing and incentives, to leave the company earlier this year — Prive aims to better enable small retailers to compete with behemoths like Amazon.
The broad idea is that by plugging into existing APIs from Shopify and other e-commerce platforms, Prive can form an opinion that it sells to merchants about what customers tend to buy on a recurrent basis. Maybe it sees that people who buy razors also tend to buy toothbrushes on a similar cadence, for example. It passes that information along, then helps the brand create more customized, and flexible, offerings so that their shoppers are presented with items they might want, as well as can more easily cancel items that are starting to pile up.
“The market opportunity is huge, and the existing [e-commerce subscription] tools are just scratching the surface,” notes Laurie. Indeed, according to the group eMarketer, subscription e-commerce sales have grown 41% from the start of the coronavirus pandemic, and it foresees that 3% of U.S. retail e-commerce sales will come from subscriptions this year, totaling $27.67 billion. That’s up from $10 billion in just two years.
Of course, a lot has yet to be built, which is where the pre-seed funding comes in. Right now, Prive is a seven-person team with some serious competition, namely from Recharge, a seven-year-old, Santa Monica, California-based subscription e-commerce company that in May raised $277 million in growth capital at a post-money valuation of $2.1 billion. As of that announcement, Recharge had roughly 330 employees and was fueling the subscription service for what it said was 15,000 merchants and 20 million subscribers worldwide.
Other rivals include nine-year-old Bold Commerce (it has raised $44 million altogether), and 10-year-old Chargebee, which has raised around $220 million over the years, according to Crunchbase data.
“E-commerce ‘subscription’ is an incredibly hot buzzword,” Craciun acknowledges. But he also thinks today’s current product offerings are just scratching the service.
Clearly, investors are willing to gamble that he’s right, and that Prive could be a team that proves it.
“Current tools can create more headaches than they actually solve,” says Craciun. “There is a lot of rigidity in today’s subscriptions that makes it very difficult to identify the right recurring mix of offerings. We’re here to break down that mental model.”
Lessons from COVID: Flexible funding is a must for alternative lenders
Contributor
Contributor
Rachael runs a bakery in New York. She set up shop in 2010 with her personal savings and contributions from family and friends, and the business has grown. But Rachael now needs additional financing to open another store. So how does she finance her expansion plans?
Because of stringent requirements, extensive application processes and long turnaround times, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) like Rachael’s bakery seldom qualify for traditional bank loans. That’s when alternative lenders — who offer short and easy applications, flexible underwriting and quick turnaround times — come to the rescue.
Alternative lending is any lending that occurs outside of a conventional financial institution. These kinds of lenders offer different types of loans such as lines of credit, microloans and equipment financing, and they use technology to process and underwrite applications quickly. However, given their flexible requirements, they usually charge higher interest rates than traditional lenders.
Securitization is another cost-effective option for raising debt. Lenders can pool the loans they have extended and segregate them into tranches based on credit risk, principal amount and time period.
But how do these lenders raise funds to bridge the financing gap for SMBs?
As with all businesses, these firms have two major sources of capital: equity and debt. Alternative lenders typically raise equity funding from venture capital, private equity firms or IPOs, and their debt capital is typically raised from sources such as traditional asset-based bank lending, corporate debt and securitizations.
According to Naren Nayak, SVP and treasurer of Credibly, equity generally constitutes 5% to 25% of capital for alternative lenders, while debt can be between 75% and 95%. “A third source of capital or funding is also available to alternative lenders — whole loan sales — whereby the loans (or merchant cash advance receivables) are sold to institutions on a forward flow basis. This is a “balance-sheet light” funding solution and an efficient way to transfer credit risk for lenders,” he said.
Let’s take a look at each of these options in detail.
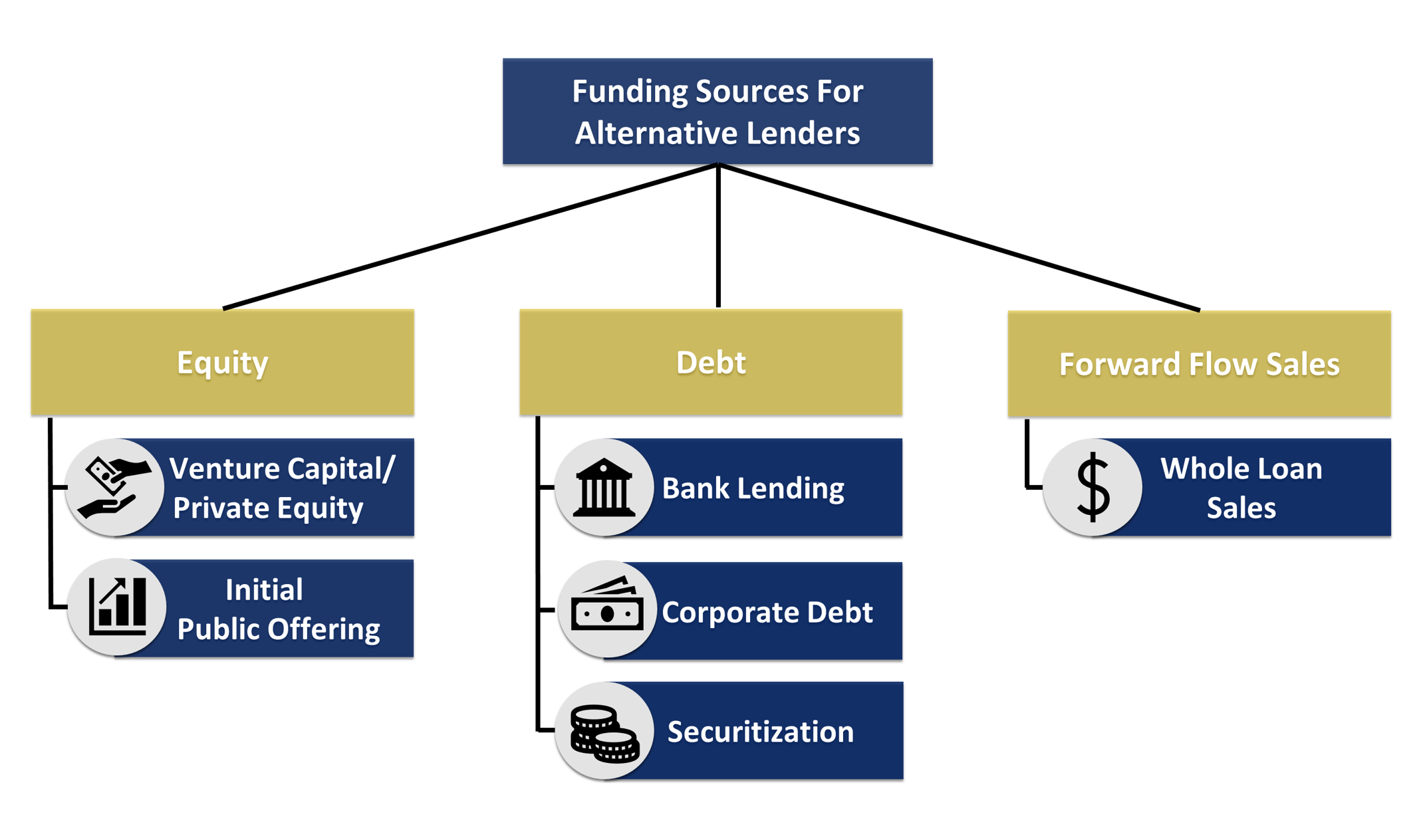
Image Credits: FischerJordan
Equity capital
Venture capital or private equity funding is one of the major sources of financing for alternative lenders. The alternative lending industry is said to be a “gold mine” for venture capital investments. While it is difficult for such companies to receive credit from traditional banks because of their stringent requirements in the initial stages, once the founders have shown a commitment by investing their own money, VC and PE firms usually step in.
However, VC and PE firms can be expensive sources of capital — their investment dilutes the ownership and control in the company. Plus, obtaining venture capital is a long, involved and competitive process.
Alternative lenders that have achieved good growth rates and scaled their operations have another option: An IPO lets them quickly raise large amounts of money while providing a lucrative exit for early investors.
Debt capital
Once the business is in good shape, banks can be more willing to lend money through loans and revolving credit facilities. Term loans are the financing provided by traditional banks, credit unions and small business administration (SBA) lenders. Although they offer low interest rates and long payment terms, they require several indicators of security, such as substantial track records and collateral, which nascent alternative lenders do not have.
Telegram tops 1 billion downloads
Popular instant messaging app Telegram has joined the elite club of apps that have been downloaded over 1 billion times globally, according to Sensor Tower.
The Dubai-headquartered app, which was launched in late 2013, surpassed the milestone on Friday, the mobile insight firm told TechCrunch. As is the case with the app’s chief rival, WhatsApp, India is the largest market for Telegram. The world’s second-largest internet market represents approximately 22% of its lifetime installs, Sensor Tower said.
“[India is] followed by Russia and Indonesia, which represent about 10% and 8% of [all installs], respectively. The app’s installs accelerated in 2021, reaching about 214.7 million installs in the first half of 2021, up 61% year-over-year from 133 million in H1 2020,” it added.
It’s worth noting that the number of installs doesn’t equate to the app’s active userbase. Telegram had about 500 million monthly active users as of early this year, for instance. But the surge in downloads, which coincides with WhatsApp’s poor handling of relaying its privacy policies to its massive userbase, nonetheless suggests that Telegram has enjoyed some additional attention in recent quarters.
Telegram, which earlier this year raised over $1 billion, is the fifteenth app worldwide to have been downloaded 1 billion times or more, Sensor Tower told TechCrunch. Other apps on the list include WhatsApp, Messenger, Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, Spotify and Netflix, according to Sensor Tower. (Mobile research firms don’t track the installs of most Google apps that come pre-installed on Android devices.)
Telegram didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment.